What you should know about gum infections
When it comes to oral hygiene, you may be concerned with preventing cavities and protecting your enamel. While it’s extremely important to take care of your teeth, you should be giving the same amount of attention to your gums as well. Your gums are the essential foundation for your teeth and should be treated with care. Poor oral hygiene and lack of care for gums can lead to periodontitis, which is a serious infection of the gums.1 By knowing how gum infections are caused and how they can be prevented, you can keep your mouth healthy as a whole.
What are some types of gum infections?
Periodontitis, which is another term for gum disease, is considered to be a serious form of gum infection that can damage the soft tissue and destroy the bone that supports your teeth if not treated.1 If you think you might have this type of gum infection, talk to your dentist immediately for treatment options. With periodontitis, your chances of reversing damage are better if you seek care immediately.1
Another oral infection that can affect the gums is an abscessed tooth. An abscessed tooth is an infection that can be caused by tooth decay, periodontal disease or a cracked tooth.3 When bacteria enters the pulp (the soft tissue within a tooth), if it’s not treated it can build up and cause a pus-filled pocket at the root tip of the tooth called an abscess.3 Symptoms of an abscess can include pain, swelling, bad taste in mouth, redness in gums or fever.3
What can happen if a gum infection is left untreated?
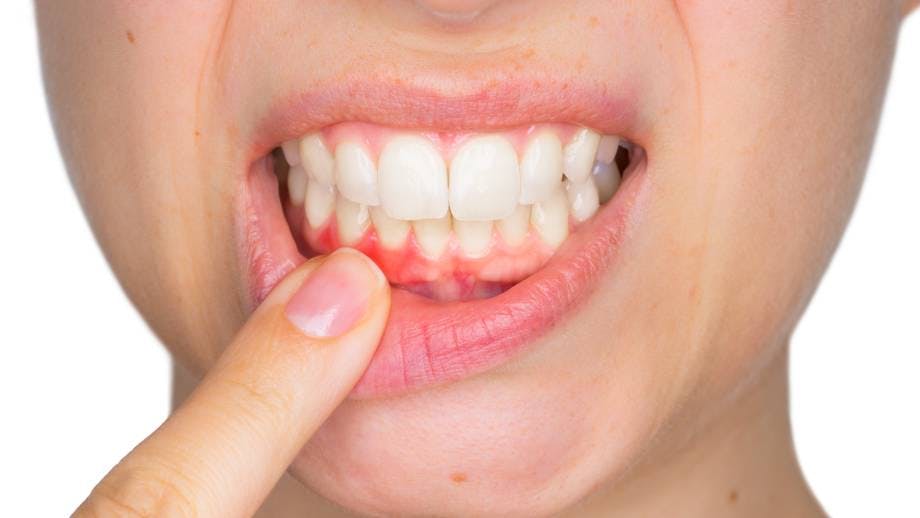
Gum disease is an untreated gum infection that can form as a result of poor oral hygiene.4 Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease, during which the gums can become swollen and red and may bleed. If gingivitis is not treated it can lead to periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease where the gums can pull away from the tooth. Bone supporting the tooth can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out.4 Gingivitis is a more mild form of gum disease than periodontitis, but both should be treated quickly before they progress.
While both conditions are serious, not all hope is lost if they are treated in a timely manner. Gingivitis can be prevented and treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning.4 The more severe form of gum disease (periodontitis) can also be treated successfully but requires more extensive treatment by a dental professional.4 Treatment will vary based on the degree of progression.
Abscesses in the mouth should not be left untreated. If the abscess does not drain, the infection can spread to your jaw and to other areas of your head and neck.2 If the infection spreads to other parts of your body, it may lead to more serious illnesses and require further care. If your immune system is weakened and you leave a tooth abscess untreated, your risk of spreading the infection increases even more.2
What causes gingival inflammation?
A common cause of gingival inflammation is plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria that rapidly builds up on your teeth. Plaque that stays on your teeth for too long can harden under your gumline into tartar, which creates a protective shield for bacteria and causes irritation along the gumline.5 There are many other risk factors that can cause inflammation of the gums. Some of these factors include smoking or chewing tobacco, dry mouth caused by drugs and medications, older age, poor nutrition/vitamin C deficiency, and hormonal changes.5
Symptoms of gum infection
Gingivitis is the first sign of gum disease, so you should be keeping an eye out for symptoms of gingivitis when checking yourself for gum infections. Some symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Swollen, puffy gums
- Gums that appear dark red
- Bleeding gums
- Receding gums, or gums that are pulling away from the teeth
Healthy gums appear firm and pale pink and are fitted tightly around the teeth.4 We look at ourselves in the mirror every day, but still may not pay close attention to how our gums look. Talk to your dentist if you notice any pain or differences in your gums.
How to treat and prevent gum infections
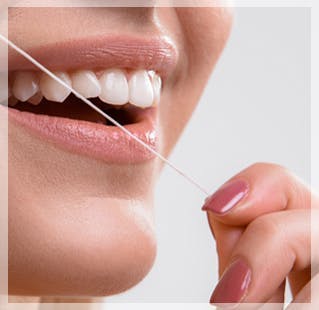
The best thing you can do to treat minor gum infections or prevent them altogether is to brush your teeth properly. Brush your teeth twice a day for at least two minutes, and remember to change out your toothbrush every three or four months.6 Use a good toothpaste like parodontax Active Gum Repair that is formulated to help reverse signs of gingivitis by targeting plaque. Make sure you are also flossing and rinsing your mouth with mouthwash to get in between your teeth for a deeper clean. It’s also a good idea to meet with your dental hygienist at least twice a year to get a thorough cleaning and an assessment of your oral health.
Every small step towards strong and healthy gums will count in the long run. Learn more about gum disease and maintaining healthy gums on the paradontax website.
SOURCES
- Periodontitis. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/periodontitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354473. Accessed 06/25/2021.
- Tooth Abscess. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901. Accessed 06/25/2021.
- Abscess (Toothache). American Dental Association. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/a/abscess. Accessed 12/15/2021.
- Periodontal Disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/conditions/periodontal-disease.html. Accessed 06/25/2021.
- Gingivitis. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gingivitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354453. Accessed 06/25/2021.
- Brushing your Teeth. American Dental Association. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/b/brushing-your-teeth. Accessed 06/25/2021.