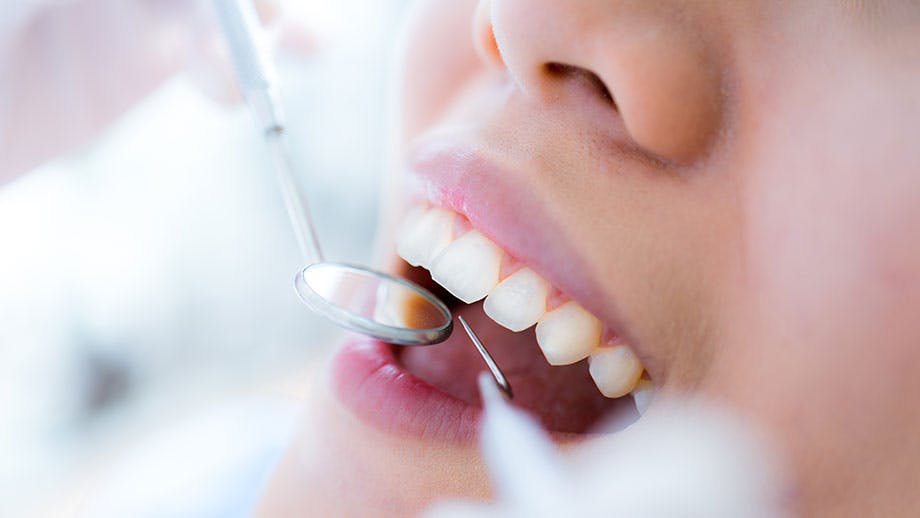
Sore gums can be caused by gingivitis, a very common and mild form of gum disease that causes gums to feel swollen, inflamed, and sore. Gingivitis is easy to treat in the early stages, but if left untreated it can turn into a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis.1 There are a number of causes for sore gums, but the most common cause is poor dental care.
What Causes Sore Gums?
The most common cause of sore gums is poor dental hygiene, which leads to the buildup of plaque.2 Plaque is a thin film of bacteria and food that sticks around your gums and teeth, and can lead to tooth decay or gum disease if not cleaned and removed properly via brushing and flossing. If you don’t keep up with your dental hygiene, plaque can harden and turn into a substance beneath your gums called tartar, which subsequently gets trapped at the base of your teeth. Symptoms of plaque and tartar buildup can include infected, swollen, and tender gums. Apart from sore gums, an excess of plaque and tartar can also lead to problems such as cavities, chronic bad breath, sore and sensitive teeth, and even periodontitis.2
However, gum pain is very common and can also be caused by brushing your teeth or gums too hard, or accidentally snapping your floss or floss pick against your gums. According to data from the CDC, 47.2% of people in the United States ages 30 and older have some form of gum disease (periodontal disease), like gingivitis or periodontitis. Gum disease increases with age, and 70.1% of adults over the age of 65 have some form of gum disease.5
Another condition that can cause sore gums is a canker sore. Canker sores are small lesions that can develop on the soft tissues in the mouth or at the base of the gums.6 Although most canker sores go away on their own after a week or two, they can be painful and make it difficult to eat or talk.6 The frequency of canker sores can be reduced by avoiding foods that irritate the mouth and following good oral hygiene habits.6
What Do Healthy Gums Look Like?
Healthy gums look firm, pink, and hug the teeth tightly without bleeding.1,2
How Can I Treat Sore Gums?
Treating and preventing sore gums is as easier than you think. You can keep your gums healthy by following these guidelines:
- Brush your teeth two times a day with a fluoride toothpaste.3 Fluoride prevents tooth decay and helps strengthen your tooth enamel. Try to brush for at least two minutes.2
- Floss after you brush your teeth to remove plaque buildup from between your teeth.
- Make time for routine visits to the dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups.3
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months, or earlier if needed. Old, used toothbrushes collect bacteria and won’t do an adequate job of cleaning your teeth. If you are using an electric toothbrush, replace the head every three to four months as well.
- Brush your teeth after eating sugary foods or avoid them if possible. Eating a healthy diet will also contribute to your gum health.
- Brush your mouthguard, dentures, or retainer often, or wash them in a cleansing solution to kill any bacteria.2
- Avoid smoking. Smoking is the most significant risk factor for gum disease and can even make treatments for gum disease less successful.3
- Be gentle with your teeth. Floss slowly and carefully and use a soft, bristled toothbrush that won’t irritate your gums.4
What is the Difference Between Sore Gums and Tooth Sensitivity
You might experience tooth pain or sensitivity from eating or drinking foods that are too hot or cold, or overly sweet or sour. Mild tooth pain or sensitivity can be attributed to a worn-down tooth or receding gums, but more severe tooth pain might be indicative of a cracked tooth, a lost filling, or a cavity. Here are some more reasons why your teeth might feel sensitive:
- An infection around the sore tooth. You might notice a small bump, or abscess, on the gums near the sore tooth, and pain in that area when you bite down.
- A tooth that has not broken through the gum tissue can cause tooth and gum pain in the affected area.
- Nerve pain in the tooth, which can be caused by things like grinding or gnashing your teeth in your sleep.4
Tooth sensitivity can also be caused by problems like:
- A sinus infection
- A migraine headache or cluster headaches
- Diabetes
- Nerve related diseases
- Drug and alcohol use, especially alcohol and methamphetamines.
- Vitamin deficiency, such as B124
Gum disease is very common in the U.S., but with these tips and a good oral hygiene routine, you can relieve your gum pain and find relief. You can use products like paradontax Active Gum Repair Toothpaste to help prevent the early signs of gum damage and target plaque, which is the main cause of gum problems.
SOURCES
- Gingivitis - Symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gingivitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354453. Accessed on 6/21/2021.
- Dental care – adult. MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001957.htm. Accessed on 6/21/2021.
- Periodontal (Gum) Disease. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/gum-disease/more-info#symptoms. Accessed on 6/21/2021.
- Toothache and Gum Problems. Michigan Medicine. https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tooth. Accessed on 12/16/2021.
- Periodontal Disease | Oral Health Conditions | Division of Oral Health. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/conditions/periodontal-disease.html. Accessed on 6/21/2021.
- Canker sore. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/canker-sore/symptoms-causes/syc-20370615 Accessed on 12/16/2021.